A New Approach to GPU Sharing: Deterministic, SLA-Based GPU Kernel Scheduling for Higher Utilization
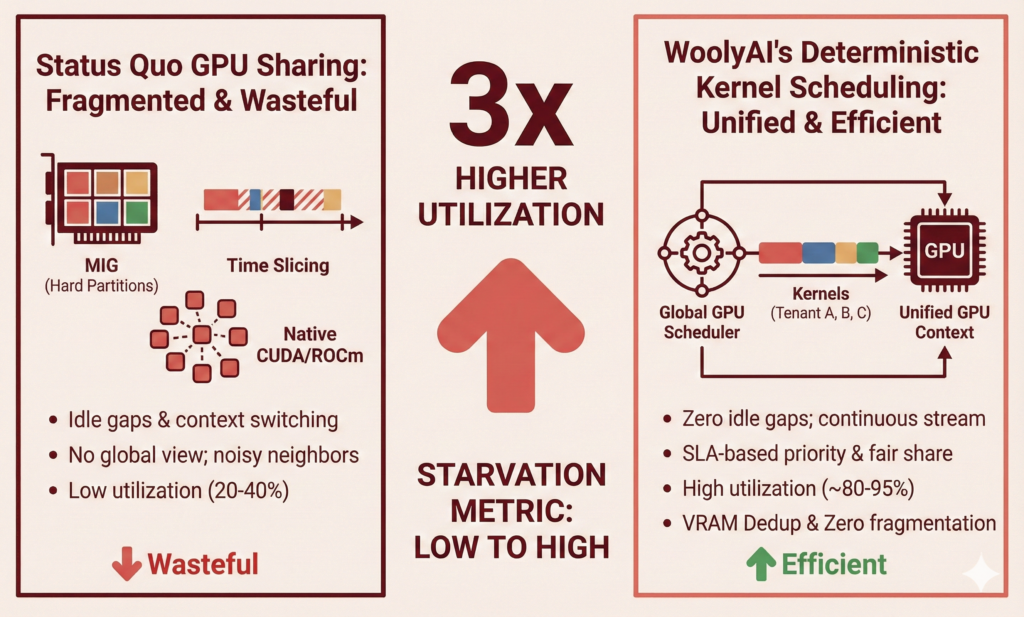
Modern GPU-sharing techniques like MIG and time-slicing improve utilization, but they fundamentally operate by partitioning or alternating access to the device—leaving large amounts of GPU compute idle and introducing latency variability. WoolyAI takes a different approach. Instead of slicing the GPU, we orchestrate GPU kernel execution directly, enabling multiple ML jobs to run concurrently inside a shared GPU context with deterministic, SLA-based scheduling. This allows the GPU to be treated as a continuously active compute fabric, maximizing SM and memory utilization while preserving predictable performance for high-priority workloads.
What WoolyAI Deterministic, SLA-Based GPU Kernel Scheduling Is
WoolyAI introduces a global, deterministic GPU scheduler that runs all tenants within a single unified GPU context, rather than letting each application run its own context.
Wooly libraries from inside the User’s ML containers intercept all framework-level ( e.g., from PyTorch) GPU operations, convert them into Wooly IR (Intermediate Representation), and routes them to the Wooly server scheduler component running on Nvidia or AMD GPU hosts that:
- JIT (Just-In-Time) compiles it to target GPU instruction set
- Orders all kernel launches across tenants
- Applies strict priority and fair-share rules
- Controls kernel pacing, concurrency, and interleaving
- Prevents any single tenant from monopolizing GPU compute
- Removes random jitter caused by native driver-level kernel contention
The result is a predictable, SLA-friendly GPU execution model where workload behavior is repeatable and tunable.
Comparison With Status Quo GPU Sharing
Approach | How It Works | Problems |
Native CUDA / ROCm (multi-process) | Each process manages its own context and streams | Idle gaps, uncontrolled concurrency, context switching, noisy neighbors |
CUDA MPS | Shares SMs across processes | Still best-effort, not deterministic, no SLA guarantees, applies to similar processes, no isolation |
MIG | Hard partitions | Rigid, wasteful, low flexibility, still no kernel-level control |
Time Slicing | Share GPU by alternating execution time | No SLA guarantees, only applies to controlled jobs, still wasteful |
Factors leading to low utilization (Status Quo)
- GPUs execute short kernels from many apps → constant idle gaps
- Python overhead + batching delays → huge underutilization
- Some tenants spike (large matmuls) → noisy neighbor interference
- No global view of GPU → drivers do non-deterministic scheduling
- VRAM fragmentation → fewer models can co-exist on a single GPU
Typical effective utilization: 20–40%.
How WoolyAI Achieves 3× Higher Utilization
WoolyAI solves all these inefficiencies through a unified execution model:
Unified GPU Context
All tenants load into one context on the GPU:
- No context switching
- Shared model weights (dedup) where applicable
- Unified memory allocator
- Zeroed fragmentation
This alone gives +30–50% more effective utilization.
Global Kernel Scheduler Removes Idle Gaps
Wooly merges all tenants’ kernel streams into one continuous GPU work queue.
When Tenant A pauses (Python, token sampling, I/O), Wooly server scheduler immediately fills that gap with work from Tenant B or C.
Wooly calculates a new metric for GPU utilization – Starvation Metric. A higher Starvation Metric means the GPU is being fully utilized efficiently across many jobs.
GPU active time rises from ~30% → ~80–95%. Check out a video demo at https://youtu.be/udps3B0KCnc
Deterministic Priority + Fair Share Scheduling
High priority tenants get execution priority with low priority interleaving when applicable.
- High-priority tenants meet consistent latency SLAs
- Background jobs do not introduce tail latency spikes
This eliminates noisy neighbors without hardware slicing.
VRAM Quotas With Weight Deduplication
Since all tenants run under one context:
- Shared Base model weights can be loaded once, especially with LoRA adapters tuned on a single base model, or SLMs tuned on a standard base foundational model.
- VRAM waste drops significantly
This increases concurrency per GPU. Check out a video Demo – https://youtu.be/o0lldESNHR4
In summary, SLA-based kernel-level GPU Scheduling transforms GPUs from single-tenant, over-reserved devices into fully utilized, multi-tenant accelerators that deliver predictable performance. It lets ML teams run far more experiments, iterate faster, and unlock higher throughput—all without buying more GPUs or rewriting a line of model code.